Learning content of sensor technology in metal and electrical professions
Functionality, application criteria, adjustment and operation of sensors are an important learning content in all occupations that come into contact with automated systems or machines.Operation, maintenance or repair of machines and systems require knowledge of sensor technology and skills in handling sensors.In automation, sensors for object detection are the most common. Pneumatic and hydraulic applications also require fluid sensors for position detection, system monitoring, energy optimization and wear diagnosis.
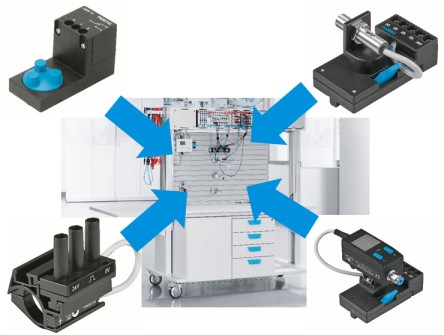
Sensors in Application Electropneumatics Basic Level TP201
- Basic concepts of sensor technology using the example of sensors for object detection
- Electrical limit switches
- Electronic proximity switches (magnetoresistive)
- Optical proximity switches
- Pressure switches (piezoresistive)
- Basic terms
- Circuit technology
- Application
- Adjustment
- Optional: object assortment, slide unit
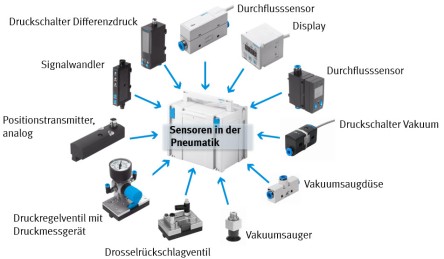
Sensors in electropneumatics TP240 assembly stage
- Non-contact position sensing
- Pressure and volume flow monitoring
- Analog output signals
- Different measuring methods
- Measurement data processing
- Special connection and circuit technology
- Signal conversion analog / binary
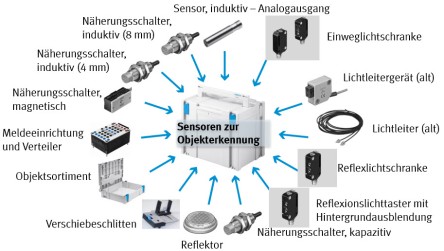
Sensors for object detection TP1311
- Magnetoresistive, optical, inductive and capacitive sensors
- Binary and analog output signals
- Design, function and parameters
- Material dependenceSelection of suitable sensors
- Logical connections

Smart Sensors TP1312
- Functions and features of intelligent sensors
- Communication protocol IO-Link
- Optical, inductive and ultrasonic sensors
- Characteristics, parameterization, condition monitoring
- Material dependence
- Adjustment in networked systems
- Signal processing in the control system
Signal processing with PLC
Learning content
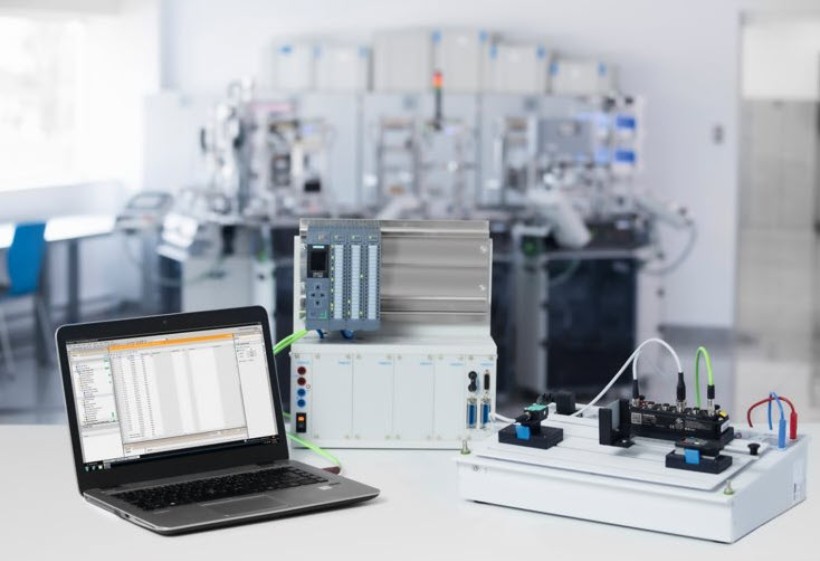

- Connection technology of binary sensors
- Connection technology of analog sensors (current / voltage)
- Signal processing of binary and analog sensors with PLC
- Establish connection to IO-Link master module or use embedded IO-Link module (depending on selected PLC option)
- Integrate process data into PLC program (properties, data structure, ...)
- Monitor and change parameters via IO-Link on a smart sensor (extended project)
Applied sensor technology
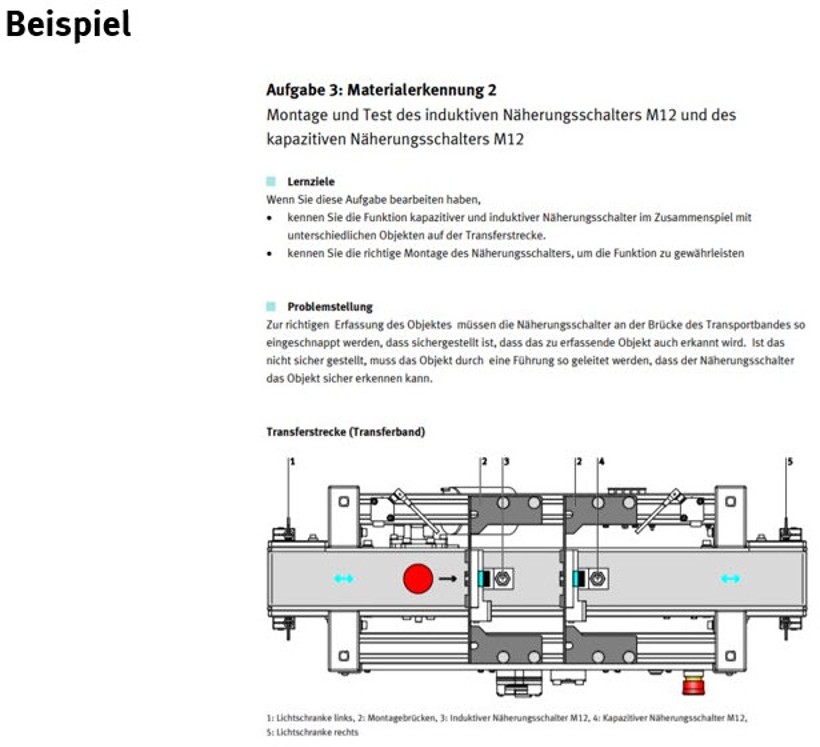
- Material detection on the MPS transfer belt or MPS Distribute Pro
- Binary, analog and intelligent sensors in application
- Selection, adjustment of sensors
- PLC programming for evaluation of sensor signals
Smart sensors in CP Lab
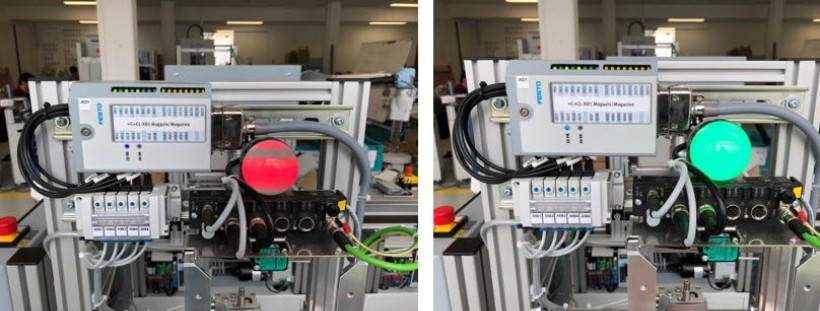
Magazine module - an IO-Link ultrasonic sensor detects the distance to the workpiece stack. In conjunction with the height of the workpieces, the fill level can be calculated precisely. An intelligent status display signals the fill level in color.
Advanced learning content

- Interconnectivity
- Operating and monitoring
- Bus controlled actuators
Building competencies in smart sensor technology for Industry 4.0
Smart sensor technology: paving the way for Industry 4.0
Through Industrie 4.0, physical operations are seamlessly integrated with software and computer-based processes into "cyber-physical systems." These systems typically use smart sensor technology at the data acquisition and monitoring level of the system architecture.
Smart sensors provide operators, technicians and engineers with meaningful information in real time. This increases productivity, efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing. Intelligent sensors form the definitive basis for Industrie 4.0 and are therefore an unavoidable topic when learning about new production environments. This applies to the basic training of apprentices as well as to the higher qualification of employees.
Smart sensors require new skills
Working with smart sensors requires more skills than with normal sensors. Operators, technicians and engineers need to understand Industrie 4.0 technology in order to take full advantage of its benefits.
Our learning path in smart sensor technology is designed to train skilled technicians. They will be able to manage, inspect, repair and troubleshoot I4.0 systems to optimize the production process.
The right tools to build skills for IO-Link sensors
For efficient learning in factory automation and mechatronics, we have developed a new set of tools: TP 1312 Intelligent Sensors. This combines industrial components with project-based learning activities.
With TP 1312, learners can develop the following skills, among others:
- Select, parameterize, monitor and adjust sensors
- Set up IO-Link communicationIntegrate sensors into various manufacturing communication layers
- Perform preventive maintenance
- Replace sensors and upload settings automatically
Tight integration with industrial networks
Smart sensors make their data available to all layers of a network (machines, PLC, SCADA, MES, ERP, cloud) using a communication protocol.
With the components of the new TP 1312 device set, you create such a network in a simplified version.