High efficiency, low emissions and no mechanical wear – fuel cells offer many advantages as sustainable suppliers of energy. They are suitable for the propulsion of vehicles, for supplying power to mobile devices, as efficient performers in stationary power plants and much more. Among their key components are bipolar plates. The electrode plates are made from metal, plastic or carbon nanotubes and are coated with a catalyst such as platinum or palladium. They separate reactant gases and cooling media from one another and distribute them to the respective reaction zones of the fuel cells. To ensure good electrical and thermal conductivity as well as resistance to chemicals and high mechanical contact pressure, bipolar plates must be of a very high quality. A new testing facility from P+K Maschinen- und Anlagenbau GmbH checks the surface finish of bipolar plates and measures their thickness. Electric cylinders EPCO with stepper motor EMMS-ST and motor controller CMMO-ST from Festo ensure the vibration-free transport of bipolar plates in the testing facility. The system was developed as part of a ZIM collaboration project by The Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Centre ZBT GmbH in Duisburg, The Society for the Advancement of Applied Computer Science in Berlin, and divis intelligent solutions GmbH in Dortmund, Germany.
Direct energy
Discovered more than 170 years ago, the development of fuel cells was for many years overshadowed by combustion engines. Although they facilitated the moon landing as an emission-free energy source in the 1960s, their potential was only brought to the attention of the wider public as the climate change debate intensified. Unlike thermal engines, fuel cells generate electrical energy directly from chemical energy. They do not need to undergo thermal processes and mechanical work first. Without the complex conversion into heat and power, fuel cells achieve a high degree of efficiency. Individual cells consist of two electrodes and a semi-permeable membrane, also referred to as a bipolar plate. Electrical energy is created through the exchange of hydrogen and oxygen electrons and protons between two electrodes.
One more question: renewable energy
The Festo expert Michael Karcher talks to the customer magazine “trends in automation”.
trends in automation: How is Festo supporting the development of renewable energy sources?
Michael Karcher, Head of Industry Segment ELA and Solar, Festo: We have been researching renewable energy production technologies at Festo since 2006. We identify processes for new technologies and develop practical solutions. These include the design of new grippers and handling systems which do not impair the surface finish of sensitive products.
trends in automation: What advantages does this offer in the area of fuel cells?
Michael Karcher: In the production of fuel cells, a low-vibration handling system can increase cycle times and thus contribute to efficient production. If we can reduce production costs, there is a better chance of renewable energy sources such as fuel cells becoming established in the market.
Contactless handling
The innovative testing facility from P+K is being used for research purposes and the development of new fuel cell production technologies for Tier 1 suppliers. The test process takes place at a total of 12 individual stations. Electric cylinders EPCO ensure low-vibration transport at and between these stations. At the first station, a Bernoulli gripper picks up the bipolar plates from a conveyor and places them on a workpiece carrier. To place the electrode plates on this carrier, a corner is opened pneumatically, the bipolar plate is placed in the carrier and the carrier is then closed pneumatically by means of a spring mechanism.
Gently does it
Next comes the visual inspection of the cooling side of the bipolar plate using a high-performance industrial camera. This is supported by bright field and dark field illumination. All types of surface defects can be identified with the help of varying lighting conditions. In the subsequent turning station turned by 180 degrees, the surface inspection of the underside, also known as the flow field side, is carried out. The testing station determines the thickness of the bipolar plates at a total of nine points. The monitor positioned above the station shows the current image of the bipolar plate and provides user-friendly, visualised access to the measurement data. The comparison with the image data shows whether the bipolar plates are of sufficiently good quality. Defective parts are ejected from the process, while the system transports the good parts to a transfer station. Here, an electric handling unit on the Z-axis places them in a magazine. Electric cylinders EPCO ensure that they are transported gently to the storage position. Thanks to their technologically sophisticated end-position cushioning, ball screw and non-rotating, plain-bearing piston rod, they prevent even the smallest amount of damage to the bipolar plates in the magazine.
Continuous transport
The fluid movement aided by electric cylinder EPCO facilitates continuous circulation of the 16 workpiece carriers in the system. This is the only way short cycle times of around four seconds can be achieved. There is no time to stop the system for image acquisition in the measurement stations. Positioning tasks are carried out in parallel with the measurements. These could lead to shock and vibration when using conventional cylinders, negatively influencing the measurement results of the cameras. This problem doesn’t occur with smooth-running electric cylinders EPCO. The cylinders also offer the advantage of extremely easy teach-in and reduce the costs associated with commissioning and product changeover.
IO-Link is used as a plant-wide bus system, from the master to all sensors and drives. All the system peripherals can thus be connected quickly and easily, significantly reducing the amount of time spent on programming. The new testing facility from P+K shows how the continuous development of process automation components in small steps can contribute to groundbreaking technologies.
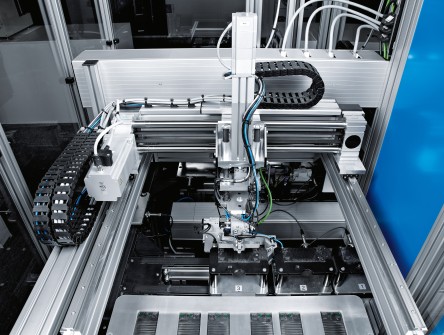
Turning the plates by 90 or 180 degrees – this is done by a pneumatic semi-rotary drive DRQD mounted on the Z-axis within the three-dimensional gantry in station 1.

A valve terminal VTUG controls all the pneumatic actuators of the system, connected to the master controller via IO-Link.
P+K Maschinen- und Anlagenbau GmbH
Schlagbaumer Straße 92a
42653 Solingen
Germany
Area of business: Design, development and production of mechanical and electrical systems, special purpose machinery, manufacturing equipment, fixture construction, assembly systems, testing stations and leak testers