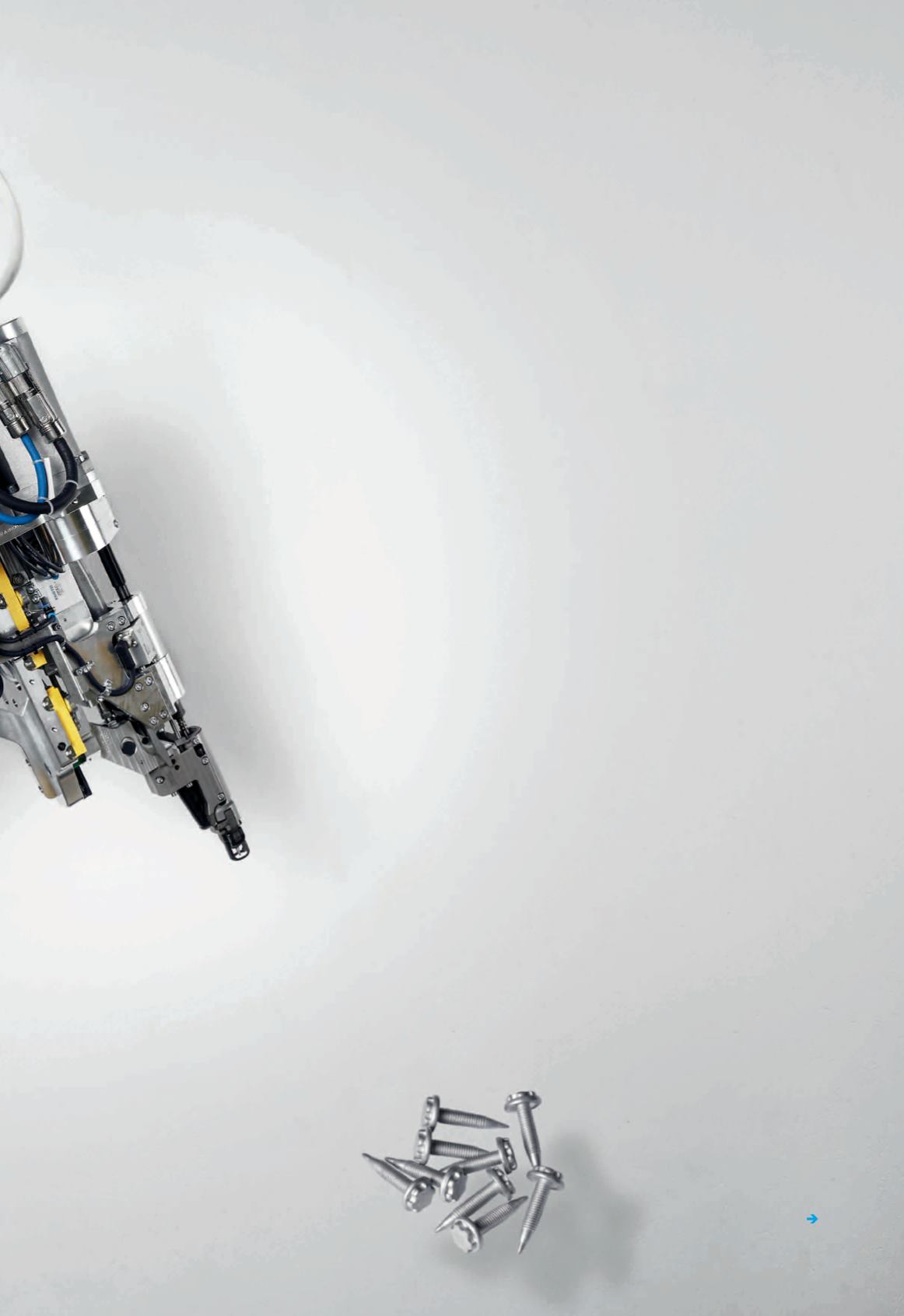
Fast and secure joining of different materials
Interaction of
forces
Along with traditional methods such as clinching and riveting,
flow drilling is
gaining in importance as a joining technology. Even steel sheets can be joined
in a single processing step without pre-drilling. The flexible parameterisation
of pressure and speed play a key role here, as demonstrated by the KFLOW
joining tool from Klingel featuring pneumatics from Festo.
L
ess moving mass, lower emissions
and increased stability mean that
lightweight construction is becom
ing increasingly important in car
production. Crucial to its success is a mix
of materials, incorporating steel, alumin
ium and carbon fibre-reinforced plastics.
Aluminium cast parts are also playing an
ever greater part. An example is the Space
Frame construction with an integrated
aluminium ladder frame which is around
40 per cent lighter than conventional
steel self-supporting bodies. These new
constructions present designers with new
challenges. How can materials be joined
quickly and reliably? Flow drilling provides
the answer to this question. This joining
technology allows different materials that
are only accessible from one side to be
joined without pre-drilling.
One company leading the way in joining
systems for flow drilling is Klingel GmbH.
Its joining systems are based on pneumatic
components from Festo. Compact, reliable
and powerful, the flow drilling systems do
their job with the help of Festo cylinders,
valves and valve terminals.
Fluid transition
The flow drilling process is a series of
seamlessly merged steps. First, the flow
drill heats the material to be joined at
high speed and with great force. Once the
material has reached the correct tempera
ture, the screw penetrates it and forms a
cylindrical hole. It then creates a nut thread
and drives through the material. Finally,
the screw is tightened with the prescribed
torque. While this may sound like a time-
consuming process, joining tools from
Klingel can complete it in 1.5 to 2 seconds.
The tool of choice is the flow drill system.
It has four zones: a hardened tip, a thread
forming zone, the screw thread and the
screw head with a recess under the head
for capturing the discharged material. The
insertion of the screw into the heated ma
terial and the resulting friction/positive
locking make it more secure after cooling.
To loosen the screw, a higher torque than
that used to tighten it is required.
1.2017
trends in automation
Synergies
26
–
27