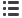
(A) The first of the three fully automated workstations
rotates the
workpiece carrier 180 degrees using a cylinder DRSL and fixes it in
place using a holding unit controlled by a mini slide DGSL.
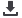
(B) Twin-piston semi-rotary drive DRRD
with three-point gripper
DHDS for picking up the workpiece for machining.
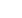
(C) A semi-rotary drive DRVS
moves two drip trays below the dosing
nozzle, thus protecting the system against contamination.
semi-automatic manual workstation and a
fully automated module with three work
stations. As the air intake controls come
off the conveyor, a rotary and swivel unit
first rotates the workpiece carrier 180 de
grees so that the information from the
reading head can be analysed. A compact
cylinder ADN designed as a holding unit
fixes the plastic housing of the air intake
control in place. A worker then inserts the
shaft for the throttle valve, which is added
later in the process. An electric linear axis
EGC moves the workpiece carrier into the
correct position for the shaft length,
which varies depending on the type. The
pneumatic linear drive DGC moves a pilot
mandrel into the end position. The shaft is
then pushed into the component with the
pilot mandrel by pressure switching. After
the joining process, the worker manually
inserts the throttle valve into the fitting
holes of the shaft.
Precision fixing
At the first of the three fully automated
workstations, the workpiece carrier is
rotated 180 degrees using a cylinder DRSL
and then fixed in place using a holding
unit controlled by a mini slide DGSL. The
next step involves checking the presence
of the needle bearing case and needle
bearing, which enclose the throttle valve
shaft on both sides. At the same time,
they are correctly aligned and positioned
so the locating pin can then be pressed in.
To ensure that the pin can be inserted at
different points, a round cylinder DSNU
moves the complete workpiece carrier
into position.
The second automated workstation first
removes the workpiece from the conveyor
using semi-rotary drive DRRD with three-
point gripper DHDS, so that the machin
ing forces do not have a negative impact
on the conveyor. After being moved to
the machining position, the ends of the
locating pins are drizzled with a synthetic
resin. To reach the pin ends on both sides
of the air intake control, the workstation
swivels the workpiece 180 degrees and
then back into the initial position. Mean
while, a semi-rotary drive DRVS moves
two drip trays below the dosing nozzle to
protect the system against contamination.
Intelligent time savings
At the third workstation for curing the
adhesive using UV light, two workpieces
can be machined at the same time. After
one workpiece has been gripped, rotated
180 degrees and transported to the UV
station, the next one can be picked up
and taken for curing. With a system cycle
time of just 13 seconds, the curing time
can be doubled. The intermediate stop
of the mini slide DGSL ensures optimum
(A)
(B)
(C)